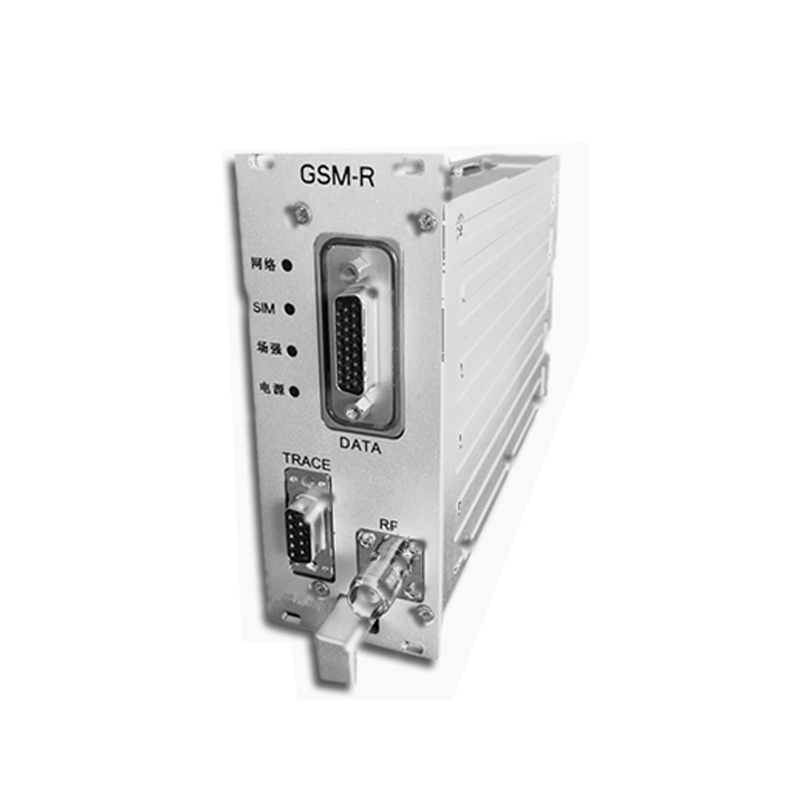
Interfaces
· 48-pin Backplane Power Connector
· 26-pin Application Device Connector
· 9-pin RS232 Maintenance Port
· TNC ‘RX/TX’ RF Connector
· 4 LED Status Indicators
· Micro 3.0V / 1.8V SIM Card Reader
· Status Indicators: Power, Network, Field, SIM
System/Standards
· Supports GSM-R frequency bands in China, Europe, India, Australia, and other regions
· Complies with China Railway CIR 2.0 and 3.0 standards
· GSM Phase 2 / Phase 2+
· Mobile Station Class B Supported
· Output Power: 1W @ 900 MHz, 1W @ 1800 MHz
Feature | Details |
Dimensions | 188.2 × 106 × 42.5 mm |
Weight | 895g |
Voltage | 12V DC |
Average Input Current | < 500mA |
Maximum Input Current | 3A |
Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +105°C |
Receiver Sensitivity | -107dBm |
Three-Level Interference Rejection | Average suppression > 40dB |
· Compliance
The introduction of GSM-R was driven by two key factors: the need to comply with the common standard for digital voice and data communications in railway operations, and the imperative to implement recommendations arising from major incident investigations.
· Improving safety
GSM-R provides continuous and direct radio communication between drivers and signallers, including in challenging environments such as tunnels and deep cuttings where traditional radio systems were ineffective. As a result, the system:
1. Enhances safety for drivers, maintenance personnel, and passengers;
2. Enables quicker and more efficient responses to potential hazards through features like the Railway Emergency Call;
3. Removes the need for drivers to leave the train in case of an incident.
· Reducing operating costs
GSM-R replaces the fragmented, outdated, and high-maintenance legacy systems, resulting in reduced operational costs, improved system reliability, and a robust platform for the development of a modern, digital railway infrastructure.
· Moving away from analogue
Previous driver–signaller communications relied on analogue radio networks, which offered limited functionality and became increasingly costly to maintain.
The adoption of digital technology enables alignment with modern railway innovations, including the European Rail Traffic Management System (ERTMS) and the European Train Control System (ETCS).